Using MySQL JDBC Driver With Spring Boot
In this article, I will show you how to connect a MySQL database with your Spring Boot application.
Tools used in this article include:
- Spring Boot 1.5.6 Release
- MySQL 5.7.X
- Maven
- Java 8
- Spring Data JPA
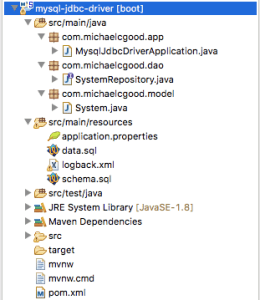
1 – Project Structure
The project structure is a typical Maven structure.
2 – Project Dependencies
Please note that the parent needs to declared. If you are using Spring Tool Suite, you can click new “Spring Starter Project” and it will populate this for you.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.michaelcgood</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>mysql-jdbc-driver</name>
<description>mysql jdbc driver example</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3 – Model
For this example application, our application will be “tracking” the last security audit of systems within a network. As this example application is meant to be simple, there will be minimal fields for the model.
Please note that there is a built in System class in the Java library. For this reason, I would avoid using System.java as a class name for a real application.
System.java
package com.michaelcgood.model;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class System {
private String name;
private Date lastaudit;
public Date getLastaudit() {
return lastaudit;
}
public void setLastaudit(Date lastaudit) {
this.lastaudit = lastaudit;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name="id")
private long id;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return id+" | " + name+ " | "+ lastaudit;
}
}4 – Repository
This is a simple CrudRepository, which is an interface that allows us to do CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
SystemRepository.java
package com.michaelcgood.dao;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.michaelcgood.model.System;
@Repository
public interface SystemRepository extends CrudRepository<System,Long> {
}5 – Database Initialization
Spring Boot enables the dataSource initializer by default and loads SQL scripts (schema.sql and data.sql) from the root of the classpath.
5.1
Here we create the SQL file that our application will use for the Table schema.
Schema.sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS system; CREATE TABLE system ( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, lastaudit DATE NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id));
5.2
We insert example values into our database.
Data.sql
INSERT INTO system(name,lastaudit)VALUES('Windows Server 2012 R2 ','2017-08-11');
INSERT INTO system(name,lastaudit)VALUES('RHEL 7','2017-07-21');
INSERT INTO system(name,lastaudit)VALUES('Solaris 11','2017-08-13');5.3
This XML file is used to configure our logging.
logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<statusListener class="ch.qos.logback.core.status.NopStatusListener" />
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<Pattern>
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n
</Pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="org.springframework.jdbc" level="error" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</logger>
<logger name="com.michaelcgood" level="error" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</logger>
<root level="error">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>6 – Configuration
We configure our datasource and JPA settings.
application.properties
#==== connect to mysql ======# spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqltutorial?useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password= spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
7 – @SpringBootApplication
CommandLineRunner is implemented in order to execute command line arguments for this example.
package com.michaelcgood.app;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import com.michaelcgood.dao.SystemRepository;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableJpaRepositories("com.michaelcgood.dao")
@EntityScan("com.michaelcgood.model")
public class MysqlJdbcDriverApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
SystemRepository systemRepository;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MysqlJdbcDriverApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Our DataSource is = " + dataSource);
Iterable<com.michaelcgood.model.System> systemlist = systemRepository.findAll();
for(com.michaelcgood.model.System systemmodel:systemlist){
System.out.println("Here is a system: " + systemmodel.toString());
}
}
}8 – Demo
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
[32m :: Spring Boot :: [39m [2m (v1.5.6.RELEASE)[0;39m
Our DataSource is = org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource@40f70521{ConnectionPool[defaultAutoCommit=null; defaultReadOnly=null; defaultTransactionIsolation=-1; defaultCatalog=null; driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; maxActive=100; maxIdle=100; minIdle=10; initialSize=10; maxWait=30000; testOnBorrow=true; testOnReturn=false; timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=5000; numTestsPerEvictionRun=0; minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=60000; testWhileIdle=false; testOnConnect=false; password=********; url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqltutorial?useSSL=false; username=root; validationQuery=SELECT 1; validationQueryTimeout=-1; validatorClassName=null; validationInterval=3000; accessToUnderlyingConnectionAllowed=true; removeAbandoned=false; removeAbandonedTimeout=60; logAbandoned=false; connectionProperties=null; initSQL=null; jdbcInterceptors=null; jmxEnabled=true; fairQueue=true; useEquals=true; abandonWhenPercentageFull=0; maxAge=0; useLock=false; dataSource=null; dataSourceJNDI=null; suspectTimeout=0; alternateUsernameAllowed=false; commitOnReturn=false; rollbackOnReturn=false; useDisposableConnectionFacade=true; logValidationErrors=false; propagateInterruptState=false; ignoreExceptionOnPreLoad=false; useStatementFacade=true; }
Here is a system: 1 | Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2017-08-11 00:00:00.0
Here is a system: 2 | RHEL 7 | 2017-07-21 00:00:00.0
Here is a system: 3 | Solaris 11 | 2017-08-13 00:00:00.0The full code is on Github
| Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Michael Good, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: Using MySQL JDBC Driver With Spring Boot Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |