Couchbase Cluster on Docker Swarm using Docker Compose and Docker Machine
This blog post will explain how to create and scale a Couchbase Cluster using full armor of Docker – Docker Machine, Docker Swarm and Docker Compose.
Here is what we’ll do:
- Create a 3-node Docker Swarm Cluster using Docker Machine
- Run a Couchbase instance on two nodes
- Create a cluster
- Rebalance the cluster
- Scale and rebalance the cluster again
Docker Swarm Cluster using Consul
Create a three-node Docker Swarm cluster using Docker Machine:
# Docker Machine for Consul
docker-machine \
create \
-d virtualbox \
consul-machine
# Start Consul
docker $(docker-machine config consul-machine) run -d --restart=always \
-p "8500:8500" \
-h "consul" \
progrium/consul -server -bootstrap
# Docker Swarm master
docker-machine \
create \
-d virtualbox \
--swarm \
--swarm-master \
--swarm-discovery="consul://$(docker-machine ip consul-machine):8500" \
--engine-opt="cluster-store=consul://$(docker-machine ip consul-machine):8500" \
--engine-opt="cluster-advertise=eth1:2376" \
swarm-master
# Docker Swarm node-01
docker-machine \
create \
-d virtualbox \
--swarm \
--swarm-discovery="consul://$(docker-machine ip consul-machine):8500" \
--engine-opt="cluster-store=consul://$(docker-machine ip consul-machine):8500" \
--engine-opt="cluster-advertise=eth1:2376" \
swarm-node-01
# Docker Swarm node-02
docker-machine \
create \
-d virtualbox \
--virtualbox-disk-size "5000" \
--swarm \
--swarm-discovery="consul://$(docker-machine ip consul-machine):8500" \
--engine-opt="cluster-store=consul://$(docker-machine ip consul-machine):8500" \
--engine-opt="cluster-advertise=eth1:2376" \
swarm-node-02
# Configure to use Docker Swarm cluster
eval "$(docker-machine env --swarm swarm-master)"Provision a Swarm cluster with Docker Machine provide more details about why and what’s done in this script. Here is a summary:
- Create a Docker Machine and run Consul for service discovery
- Create three Docker Machines – one for Master and two for Worker nodes.Each machine is configured to be part of a Swarm cluster using
--swarm. It also uses the Consul service discovery specified using--swarm-discovery.
Couchbase Nodes on Docker Swarm
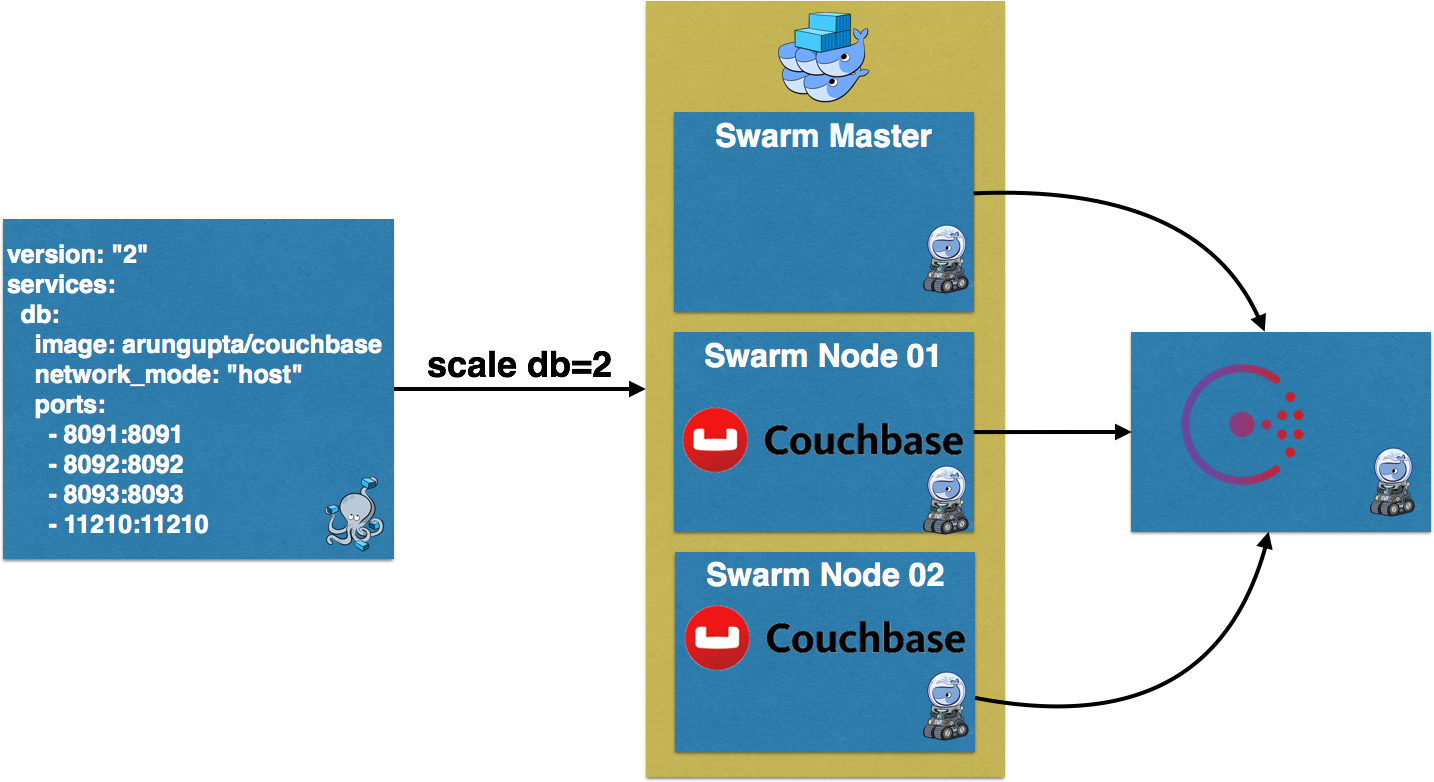
Create two instances of Couchbase using Docker Compose:
version: &2&
services:
db:
image: arungupta/couchbase
network_mode: &host&
ports:
- 8091:8091
- 8092:8092
- 8093:8093
- 11210:11210arungupta/couchbase image is used here. This image is defined at Couchbase Docker Image. It uses the Official Couchbase Docker Image add configures it as explained:
- Setups memory for Index and Data
- Configures the Couchbase server with Index, Data, and Query service
- Sets up username and password credentials
- Loads the
travel-samplebucket
Compose file uses host network. This is equivalent to using --net=host on docker run CLI. It allows the container to use the host networking stack. It also limits only a single Couchbase container to run on a single Docker Machine. So this means that our Couchbase cluster can scale based upon the number of Docker Machines – 3 in our case.
The exact command to use this Compose file is:
docker-compose scale db=2 WARNING: The "db" service specifies a port on the host. If multiple containers for this service are created on a single host, the port will clash. Creating and starting couchbasedockerswarm_db_1 ... Creating and starting couchbasedockerswarm_db_2 ... Pulling db (arungupta/couchbase:latest)... swarm-node-02: Pulling arungupta/couchbase:latest... swarm-master: Pulling arungupta/couchbase:latest... swarm-node-01: Pulling arungupta/couchbase:latest... Pulling db (arungupta/couchbase:latest)... swarm-node-02: Pulling arungupta/couchbase:latest... : downloaded Creating and starting couchbasedockerswarm_db_1 ... done Creating and starting couchbasedockerswarm_db_2 ... done
There are three nodes in the Docker Swarm cluster. The default scheduler strategy is spread and so the containers will be spread on different hosts.
This is evident by docker ps:
docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4c8c149f4e34 arungupta/couchbase &/entrypoint.sh /opt/& 44 seconds ago Up 44 seconds swarm-node-02/couchbasedockerswarm_db_1 d3b6a1dbddb5 arungupta/couchbase &/entrypoint.sh /opt/& 44 seconds ago Up 44 seconds swarm-node-01/couchbasedockerswarm_db_2
Note, one Couchbase server is running on swarm-node-01 and another on swarm-node-02. Each server is configured with an administrator username Administrator and password password.
Find out IP address of the Docker Machine:
docker-machine ls NAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARM DOCKER ERRORS consul-machine - virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.106:2376 v1.11.1 default - virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.100:2376 v1.11.0 swarm-master * (swarm) virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.107:2376 swarm-master (master) v1.11.1 swarm-node-01 - virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.108:2376 swarm-master v1.11.1 swarm-node-02 - virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.109:2376 swarm-master v1.11.1
If you have jq installed then IP address can be conveniently found as:
docker-machine inspect swarm-node-01 | jq &.Driver.IPAddress& &192.168.99.108&
Couchbase Cluster on Docker Swarm
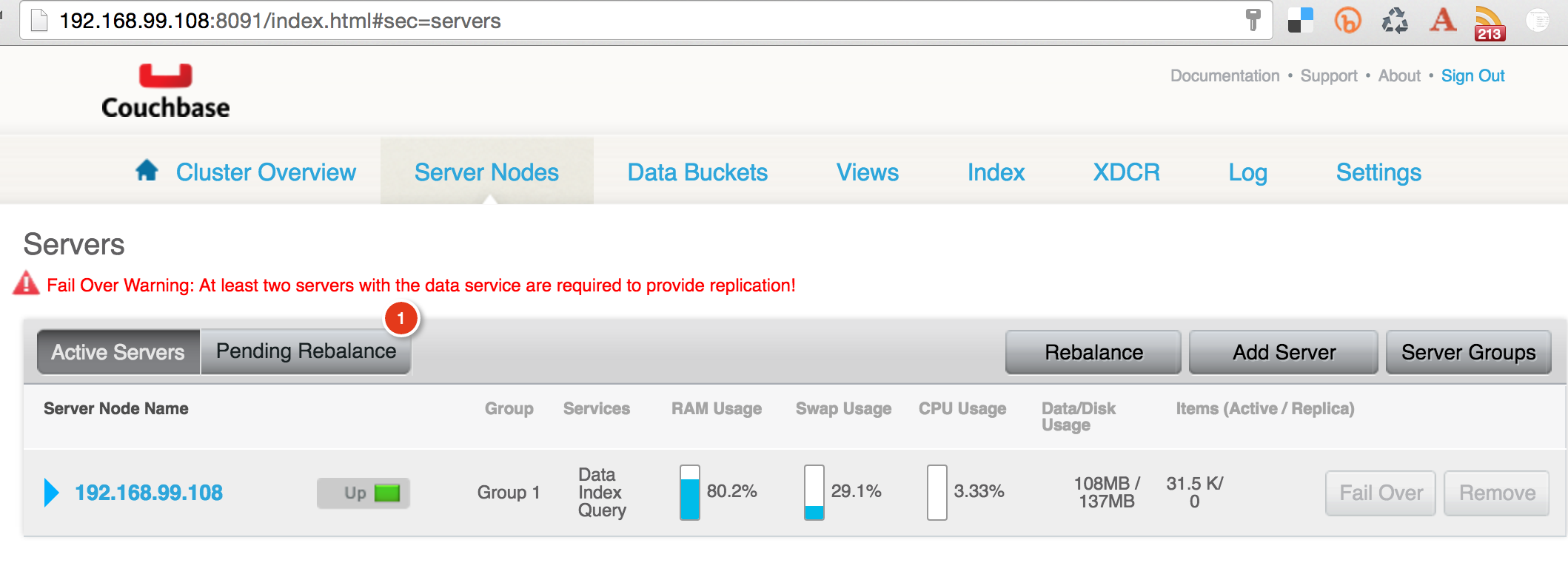
All Couchbase server nodes are created equal. This allows the Couchbase cluster to truly scale horizontally to meet your growing application demands. Independently running Couchbase nodes can be added to a cluster by invoking the server-add CLI command. This is typically a two step process. The first step is adding one or more nodes. The second step then rebalances the cluster where the data on the existing nodes is rebalanced across the updated cluster.
In our case, a single Couchbase container is running on each Docker Machine. Lets pick IP address of any one Couchbase node, and add IP address of the other node:
docker run -it arungupta/couchbase \ couchbase-cli \ server-add \ --cluster=`docker-machine inspect swarm-node-01 | jq -r &.Driver.IPAddress&`:8091 \ --user Administrator \ --password password \ --server-add=`docker-machine inspect swarm-node-02 | jq -r &.Driver.IPAddress&` \ --server-add-username=Administrator \ --server-add-password=password SUCCESS: server-add 192.168.99.109:8091
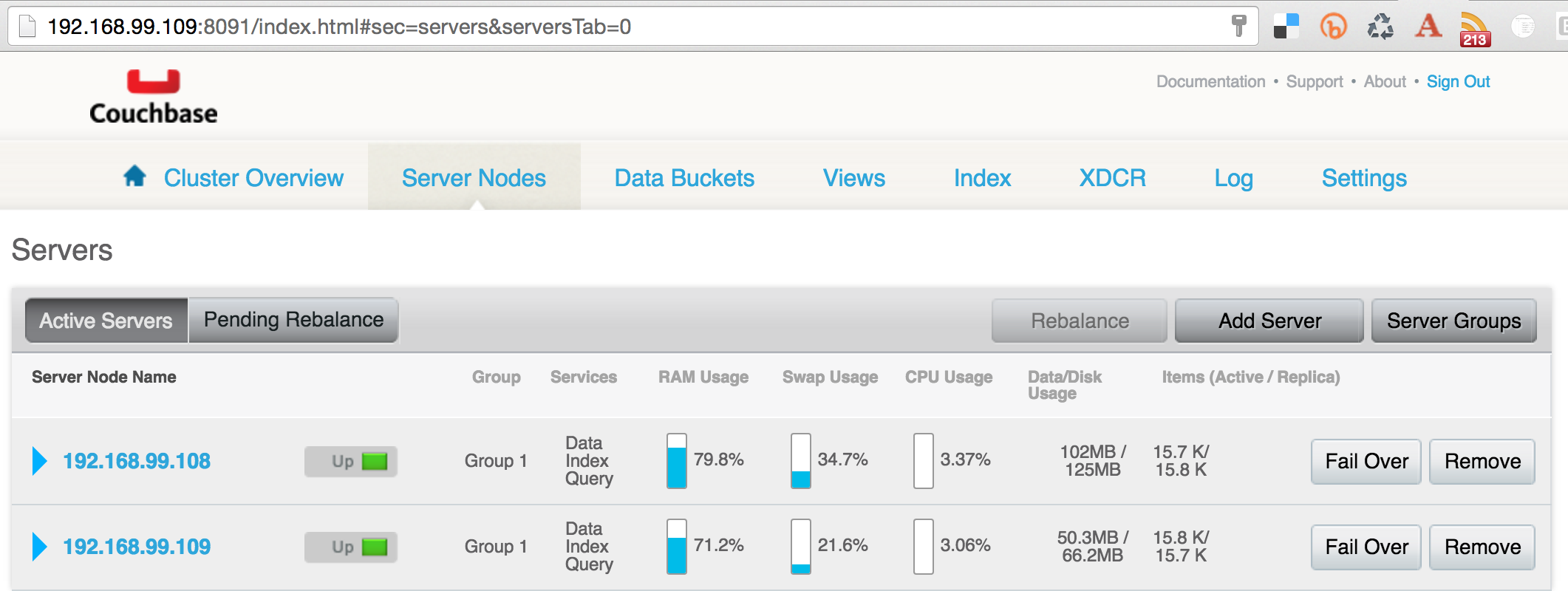
Couchbase Web Console for both the nodes will show a similar output:
This shows that the two nodes now form a cluster, and needs to be rebalanced.
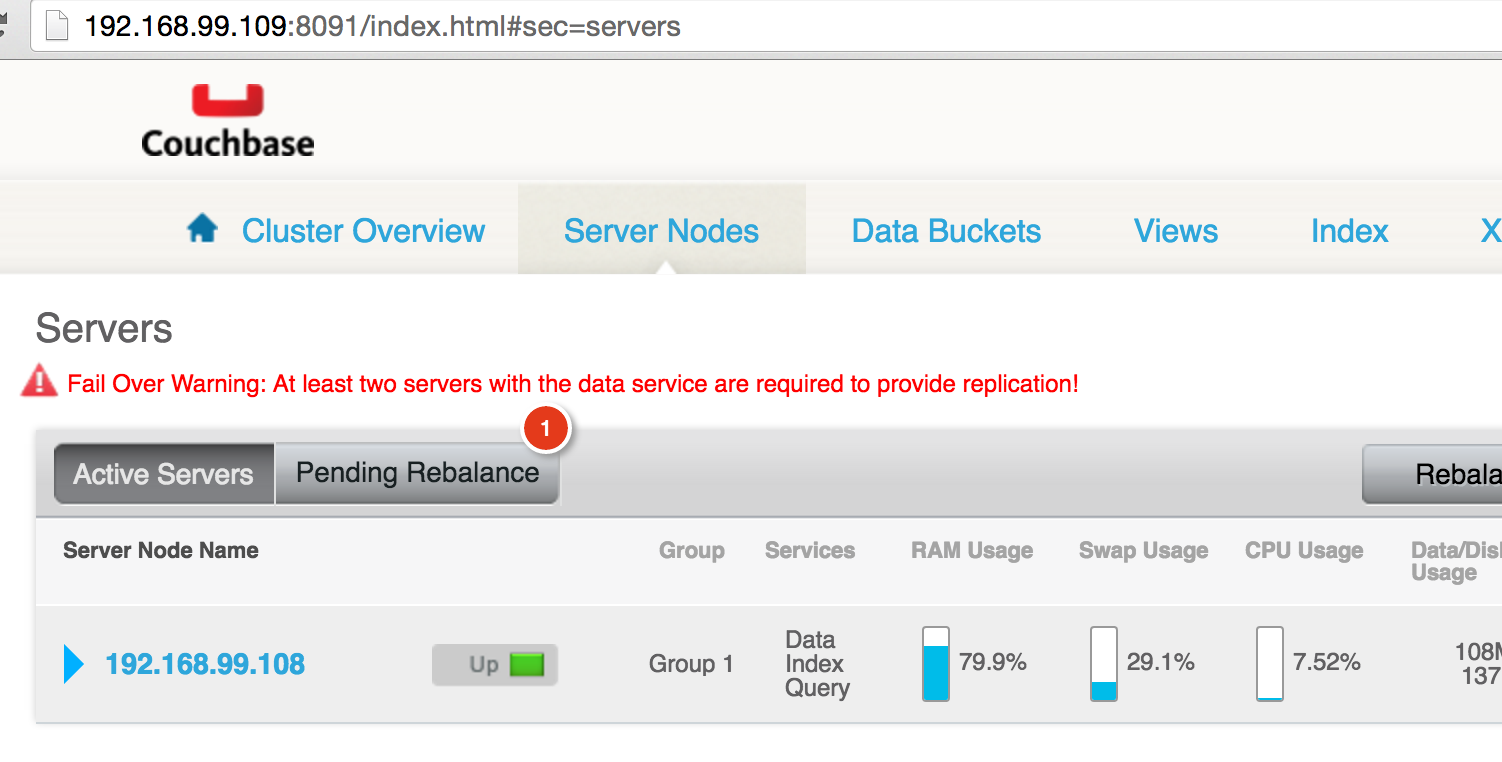
Rebalance Couchbase Cluster
Now, lets rebalance the cluster:
docker run -it arungupta/couchbase couchbase-cli rebalance --cluster=`docker-machine inspect swarm-node-01 | jq -r &.Driver.IPAddress&`:8091 --user Administrator --password password INFO: rebalancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . SUCCESS: rebalanced cluster
Couchbase Web Console will be updated to show that rebalance is happening:
And finally you’ll see a rebalanced cluster:
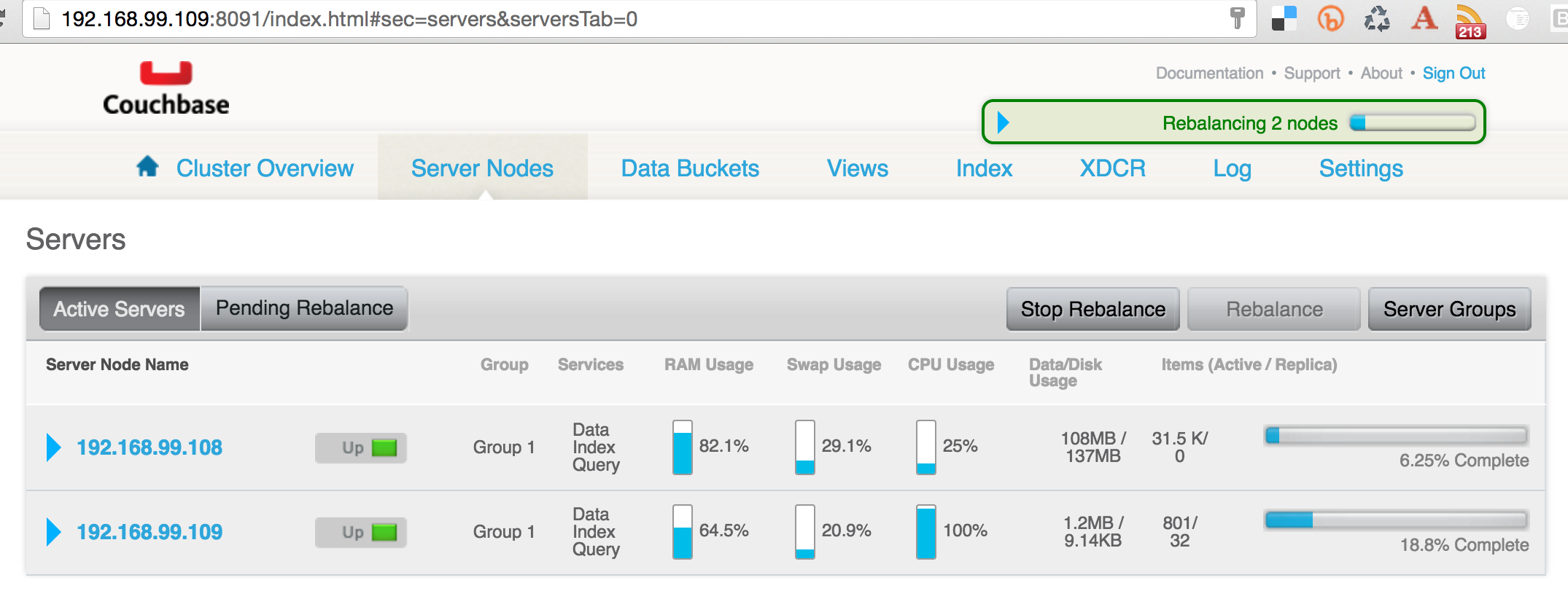
Scale and Rebalance Couchbase Cluster
Scale the Couchbase cluster:
docker-compose scale db=3 WARNING: The &db& service specifies a port on the host. If multiple containers for this service are created on a single host, the port will clash. Creating and starting couchbasedockerswarm_db_3 ... done
Check that the container is running on a different Docker Machine:
docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 02f94e2bbd3e arungupta/couchbase &/entrypoint.sh /opt/& 9 seconds ago Up 8 seconds swarm-master/couchbasedockerswarm_db_3 4c8c149f4e34 arungupta/couchbase &/entrypoint.sh /opt/& About an hour ago Up About an hour swarm-node-02/couchbasedockerswarm_db_1 d3b6a1dbddb5 arungupta/couchbase &/entrypoint.sh /opt/& About an hour ago Up About an hour swarm-node-01/couchbasedockerswarm_db_2
As mentioned earlier, scaling a Couchbase cluster is a two-step process. This is so because typically you’ll add multiple servers and then rebalance the cluster. However, in cases where you only need to add a single Couchbase node and then rebalance, the rebalance command can be used achieve that.
In our case, this is done as shown:
docker run -it arungupta/couchbase couchbase-cli rebalance --cluster=`docker-machine inspect swarm-node-01 | jq -r &.Driver.IPAddress&`:8091 --user Administrator --password password --server-add=`docker-machine inspect swarm-master | jq -r &.Driver.IPAddress&` --server-add-username=Administrator --server-add-password=password SUCCESS: server-add 192.168.99.107:8091 INFO: rebalancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . SUCCESS: rebalanced cluster
The rebalanced cluster now looks like:
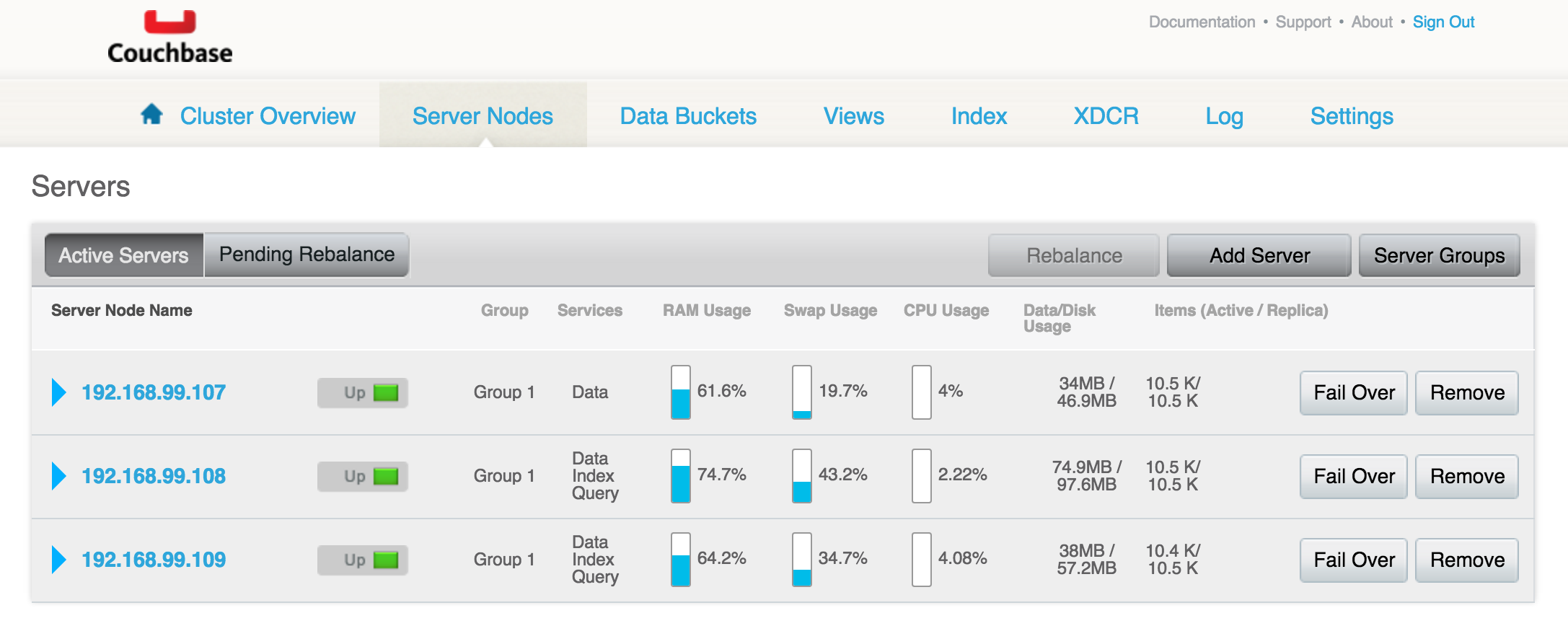
This blog showed how you can easily create and scale a Couchbase Cluster using Docker Swarm, Machine and Compose.
Enjoy!
| Reference: | Couchbase Cluster on Docker Swarm using Docker Compose and Docker Machine from our JCG partner Arun Gupta at the Miles to go 3.0… blog. |