Tomcat Clustering Series Part 2 : Session Affinity Load Balancer
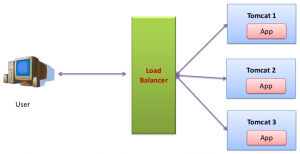
This is the second part of the Tomcat Clustering Series. In the first part we discussed how to setup a simple load balancer. And we saw how the load balancer distributes the requests to tomcat instances in a round robin fashion. In this post we talk about what is the problem that occurs in the simple load balancer when we introduce sessions in our web application. And we will see how to resolve this issue.
How Session works in Servlet/Tomcat?
Before going into the problem, let’s see the session management in Tomcat.
If any of the pages/servlets creates a session, then Tomcat creates the Session Object and attaches is into the group of sessions (HashMap-like structure) and that session can be identified by using the session-id, which is just a random number generated through any one of the hash algorithms. Then responds to client with a cookie header field. That cookie header field is a key-value pair. So tomcat creates jsessioid which is the key and the random session-id is the value.
When the response reaches the client (Web Browser), it updates the cookie value. If it already exists, then it overrides the cookie value. From now on, the browser sends the cookie attached with the request to that server.
HTTP is a stateless protocol. So the server can’t find the client session trivially. So the server reads the header of the request and extracts the cookie value and the Random session-id. Then it search through the group of session maintained by Tomcat. Then tomcat gets the Session of that particular client (Web Browser).
If the client cookie value doesn’t have a match in the group of sessions, then Tomcat creates a completely new session and sends the new cookie to the browser. Then the browser updates it.
This index.jsp code is to deploy all tomcat instances.
<%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%>
<%@page import="java.util.Date"%>
<%@page import="java.util.List"%>
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>JSP Page</title>
<font size="5" color="#0000FF">
Instance 1
</font>
<hr>
<font size="5" color="#CC0000">
Session Id : <%=request.getSession().getId()%>
Is it New Session : <%=request.getSession().isNew()%>
Session Creation Date : <%=new Date(request.getSession().getCreationTime())%>
Session Access Date : <%=new Date(request.getSession().getLastAccessedTime())%>
</font>
<b>Cart List </b>
<hr>
<ul>
<%
String bookName = request.getParameter("bookName");
List<string> listOfBooks = (List<string>) request.getSession().getAttribute("Books");
if (listOfBooks == null) {
listOfBooks = new ArrayList<string>();
request.getSession().setAttribute("Books", listOfBooks);
}
if (bookName != null) {
listOfBooks.add(bookName);
request.getSession().setAttribute("Books", listOfBooks);
}
for (String book : listOfBooks) {
out.println("<li>"+book + "</li>
");
}
%>
</string></string></string></ul>
<hr>
<form action="index.jsp" method="post">
Book Name <input type="text" name="bookName">
<input type="submit" value="Add to Cart">
</form>
<hr>
What is the Problem in the Simple Load Balancer?
If we deploy the web application, in which its uses the session, then actually the problem occurs.
I describe with sequence
- User request one web page, in that web page its used sessions (like shopping cart).
- Load balancer intercept the request and use the round robin fashion its send to one of the tomcat. suppose this time its send to tomcat1.
- tomcat1 create the session and respond with cookie header to client.
- load balancer just act as relay. its send back to client.
- next time user request again the shopping cart to server. this time user send the cookie header also
- Load balancer intercept the request and use the round robin fashion its send to one of the tomcat. this time its send to tomcat2.
- Tomcat 2 receive the request and extract the session-id. and this session id is doesn’t match with their managed session. because this session is available only in tomcat1. so tomcat 2 is create the new session and send new cookie to client
- Client receive the response and update the cookie(Its overwrite the old cookie).
- Client send one more time to request that page and send the cookie to server.
- Load balancer intercept the request and use the round robin fashion its send to one of the tomcat. this time its send to tomcat3.
- Tomcat 3 receive the request and extract the session-id. and this session id is doesn’t match with their managed session. because this session is available only in tomcat2. so tomcat3 is create the new session and send new cookie to client
- Client receive the response and update the cookie.(Its overwrite the old cookie).
- Client send one more time to request that page and send the cookie to server.
- Load balancer intercept the request and use the round robin fashion its send to one of the tomcat. this time its send to tomcat1.
- Tomcat 1 receive the request and extract the session-id. and this session id is doesn’t match with their managed session. because client session id is updated by tomcat 3 last time. so even though tomcat 1 have one session object created by this client. but client session id is wrong.so tomcat3 is create the new session and send new cookie to client (for more info watch the video below)
- Client receive the response and update the cookie.
This sequence continues …
As a result, on every request one new session is created. Instead of continuing with the old one.
Here the root cause is the Load balancer. If the load balancer redirects the request correctly then this problem is fixed. But how the load balancer knows in advance about this client before it is processed by a particular Tomcat instance.
HTTP is a stateless protocol. So HTTP doesn’t help this situation. And the other information is the jsessionid cookie. It’s good but it’s just a random value. So we can’t take the decision based on this random value.
ex:
Cookie: JSESSIONID=40025608F7B50E42DFA2785329079227
Session affinity/Sticky Session
Session affinity overrides the load-balancing algorithm by directing all requests in a session to a specific Tomcat server. So when we setup the session affinity our problem is solved. But how to setup this, the problem is that the session values are random value. So we need to generate the session value, to somehow identify which Tomcat instance generates the response.
jvmRoute
The Tomcat configuration file (server.xml) contains an <Engine> tag thas has jvmRoute attribute for this purpose. So, edit the config file and update the <Engine > tag like this
<Engine name='Catalina' defaultHost='localhost“ jvmRoute=“tomcat1” >
here we mention jvmRoute=’tomcat1′
Here tomcat1 is a worker name of this Tomcat instance. Check the workers.properties file in last post.
Add this line to all Tomcat instances conf/server.xml file and restart the Tomcat instances.
Now all Tomcat instances generate the session-id pattern like this
<Random Value like before>.<jvmRoute value>
ex:
Cookie:JSESSIONID=40025608F7B50E42DFA2785329079227.tomcat1
Here, in the end of the value, we can see which Tomcat instance has generated this particular session. So the load balancer can easily find out where we need to delegate the request. In this case it’s tomcat1.
So, update all tomcat instances conf/server.xml file to add the jvmRoute property to appropriate worker name values. and restart the instances. All problems are fixed and the entire load balance works fine even in session based application. But there is still one drawback
Let’s say tha 5 users are accessing the website. The session affinity is setup. Here
tomcat 1 serves 2 user,
tomcat 2 serves 2 user,
tomcat 2 serves 1 user, then suddenly one of the instances fails. Then what happen?
Suppose instance 1 (tomcat1) failed, then those 2 users have lost their session. But their requests are redirected to one of the remaining tomcat instances (tomcat2,tomcat3). So they still access the web page. But they lost the previous sessions. This is one of the drawbacks. But compared to the last post load balancer it works in session based web application also.
In the next post we will see how to set up the session replication in load balancer.
Video
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=-9C2ZtdAAFY
Reference: Tomcat Clustering Series Part 2 : Session Affinity Load Balancer from our JCG partner Rama Krishnan at the Ramki Java Blog blog.