Enterprise Java
Java EE CDI Qualifiers: Quick Peek
Qualifiers are the mainstay of type safety and loose coupling in Contexts and Dependency Injection (CDI). Why? Without CDI, we would be injecting Java EE components in a manner similar to below
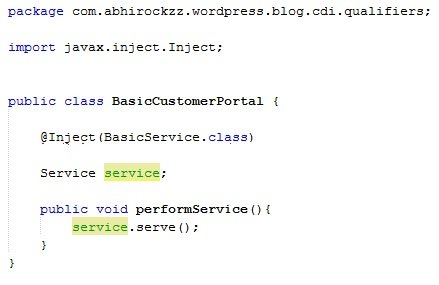
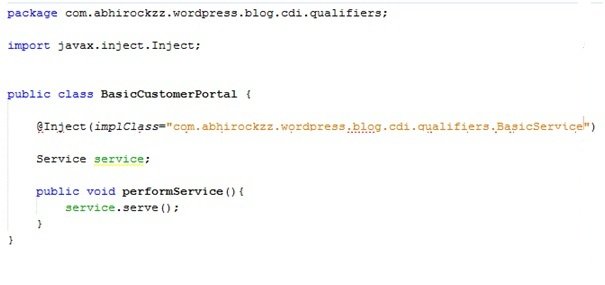
Note:This will actually not compile and is just a hypothetical code snippet
Example 1
Example 2
What’s wrong with the above implementations?
- Not type safe – Uses a String to specify the fully qualified name of an implementation class (see Example 1)
- Tightly couples the BasicCustomerPortal class to the BasicService class (see Example 2)
This is exactly why CDI does not do Injection this way !
Qualifiers help promote
- Loose Coupling – An explicit class is not introduced within another. Detaches implementations from each other
- Strong Typing (type safety) – No String literals to define injection properties/metadata
Qualifiers also serve as
- Binding components between beans and Decorators
- Event selectors for Observers (event consumers)
How to use Qualifiers?
CDI Qualifiers Simplified
Simplified steps
- Create a Qualifier
- Apply Qualifiers to different implementation classes
- Use the Qualifiers along with @Inject to inject the instance of the appropriate implementation within a class
This was not a detailed or in-depth post about CDI Qualifiers. It’s more of a quick reference.
More on CDI
Thanks for reading!
| Reference: | Java EE CDI Qualifiers: Quick Peek from our JCG partner Abhishek Gupta at the Object Oriented.. blog. |