Release Planning Advice
Release planning is an important task for product people working with agile teams: It ensures that the product is moving in the right direction and it connects strategy and tactics. Despite its importance, release planning is not always effectively practiced in my experience. This article shares my advice to help you reflect on your release planning practices and improve them.
What Release Planning Entails and Why It Matters
While release and release planning are common terms, I find that different individuals attribute different meanings to them. I regard a release as a version of a product, for example, Mac OS X Catalina and Windows 10. Releases come in two flavours: major releases, like iOS 13, and minor releases, such as iOS 13.3.
Release planning is the process of determining the desired outcome of one or more major releases and maximising the chances of achieving it. This involves the following:
- Establishing clear, specific, and measurable goals. I call these goals product or release goals and I capture them on a product roadmap.
- Determining the work to be done. This typically involves the development team providing rough, high-level estimates.
- Understanding date and budget constraints: Are there any hard deadlines that must be met, or is the budget fixed?
- Monitoring progress from sprint to sprint and making adjustments as required. In Scrum, release planning is carried out iteratively, often at the end of a sprint when it’s clear how much the progress was made.
Release planning enables organisations to make informed investment decisions; it sets expectations, aligns stakeholders and development teams; and it allows product people to guide the work of the dev team.
It is therefore in your best interest—as the person in charge of the product—to make sure that release planning is effectively carried out. This requires you to actively engage in the work, rather than delegating it to the development team or Scrum Master.
Use a Product Roadmap to Plan Multiple Releases
Release planning takes place at two levels: across several major releases and within a single release. The former can be nicely done with a product roadmap. My preference is to work with a goal-oriented roadmap, like my GO Product Roadmap shown below, that states the desired benefits or outcomes of each major release for the next 12 months. Sample goals include acquiring new users, increasing conversion, reducing cost, and removing technical debt to future proof the product.

The goals on your product roadmap should tell a compelling story about the likely development of your product. They should describe the journey you want to take it on in order to create value for the users and the business, as I explain in more detail in the article “Product Roadmap Prioritisation”. Such a roadmap provides a continuity of purpose and ensure that individual releases build on each other thereby progressing and enhancing the product in a systematic way. What’s more, the roadmap goals help you focus the product backlog by limiting its content to items that are necessary to meet the next release goal.
But don’t forget to regularly review the product roadmap—at least once every three months, as a rule of thumb. As you learn more about the development team’s ability to make progress and better understand how to best meet the user and business needs, you will need to update your roadmap. This ensures that the plan stays actionable and provides the necessary guidance to the stakeholders and dev team.
Prioritise the Success Factors for Your Releases
In an ideal world, the development team will deliver all the releases on the product roadmap on time and on budget. But in reality, unforeseen things do happen. The development progress may not be as fast as anticipated, for instance, or one of the technologies may not work as expected.
To maximise the chances of success, I recommend that you prioritise goal, date, and budget for the releases captured on your product roadmap. One way to do this is to determine the impact of not (fully) meeting a goal, missing the desired release date, and exceeding the budget. Then fix the most important factor—the factor that would cause the biggest damage if you don’t adhere to and therefore has the biggest impact on the success of the product. Try to protect the second most important factor, the one that would create the second biggest damage. Finally, be flexible with the third one, the factor that has the least impact on the success of a major release.
You might have noticed that I haven’t mentioned quality. There’s a reason for it: Quality should be fixed and not be compromised. Otherwise, responding to user feedback and changing market conditions and quickly adapting your product will be hard, if not impossible.
Employ the Right Estimation Approaches
Estimating the cost of the releases on your product roadmap is helpful to acquire the necessary budget or, if your budget is fixed, understand if the roadmap is realistic and actionable—if the development team can actually implement it. Rough, high-level estimates are usually sufficient to meet this objective.
To come up with the estimates, draw on your experience of developing similar products or previous versions of the same product; consider whether enough people with the right expertise are available in your company, or if you will have to hire or contract people. This should give you an indication of the likely labour cost required. Then add the cost for facilities, infrastructure, materials, licenses, and other relevant items. Carry out this exercise together with the development team.
If you believe that the resulting estimates will be too vague, consider the alternative: Breaking the roadmap features upfront into epics and user stories will result in a long, detailed product backlog that is difficult to adjust and maintain. Additionally, this process can take days—and in some cases weeks—in my experience. And while you will get more detailed estimates, they will not be accurate at this stage.
Once you have secured the necessary budget and ensured that the releases on your roadmap are realistic, take the next step and stock the product backlog. As I explain in the article “The Product Roadmap and the Product Backlog”, I like to focus the backlog on the upcoming release and the next roadmap goal. To follow this approach, derive epics from the features that belong to the appropriate goal. Then explore which additional pieces of functionality the release has to offer and add them as epics to the product backlog. Finally, prioritise the items and refine the high-priority ones. This should result in a concise, compact backlog that is comparatively easy to adapt and that offers enough ready, high-priority items. Don’t forget to involve the development team in this exercise.
Additionally, ask the team to estimate the product backlog items. This might be done by using story points and Planning Poker, as explained in Mike Cohn’s book Agile Estimating and Planning.
Use a Release Burndown Chart to Track Progress
The release burndown chart is a simple yet powerful tool to track and forecast the progress for a release. Despite its usefulness, experience tells me that many Scrum product owners don’t use the burndown. But creating the chart is simple. Start by asking the development team to estimate the total amount of the product backlog items that should be part of the release. Rough, high-level estimates are sufficient. Then draw a coordinate system that takes into account time, captured as sprints, and effort in the product backlog, which might be expressed as story points.
The first data point is the estimated effort before any development has taken place. To arrive at the next data point, determine the remaining effort in the product backlog at the end of the first sprint. Then draw a line through the two points. This line is called the burndown. It shows the rate at which the effort in the product backlog is consumed. It is influenced by two factors: changes in the product backlog and velocity, which is the development team’s ability to make progress. Extending the burndown line to the horizontal axis allows you to forecast when the development effort is likely to finish, or if you are likely to reach the release goal and deliver all relevant product backlog items at a specific date.
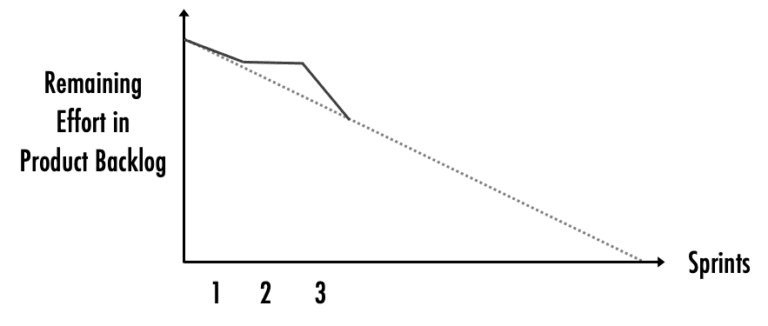
The release burndown chart above shows two lines. The solid line is the actual burndown. It documents the progress to date and the effort remaining. The dotted one is the forecasted progress based on the burndown experienced so far. Notice that the burndown in the second sprint is flat. This might be caused by new items being added to the product backlog or the dev team revising estimates.
To achieve a forecast that is as accurate as possible, try the following three tips:
- Base your forecast on a trend rather than a single sprint. This usually requires you to run two to three sprints before you can create the first forecast for a release.
- Consider how representative the burndown of the past sprints is for the remaining sprints. In the example shown above, the second sprint has a flat burndown. This might be due to more items being added to the product backlog based on the first sprint review meeting or the dev team re-estimating items. To get the forecast right, it would be worth considering how likely it is that another flat burndown will occur again and to which extent you should account for it. If you decided that it was highly unlikely to reoccur, your forecast in the sample chart above would probably be steeper.
- Make sure that you prioritise the product backlog by risk, particularly in the early sprints. This makes it more likely that the backlog changes in the first few sprints and then starts to stabilise. This makes forecasting the remainder of the development effort easier and results in a more accurate forecast.
If the forecast shows that you are off-track, that the burndown is slower than anticipated, then determine the causes. For example, the development team might lack some crucial skills, the team might be too small, a technology might not work as expected, you might have been too optimistic, or the initial estimates might have been wrong. Once you’ve identified the main cause, decide how to respond. The prioritisation of goal, time, and cost recommended above will help you with this.
Note that if you have to push out the release date or make a bigger change to the goal of the release, this may have an impact on your product roadmap and require you to adjust it.
Make Release Planning Collaborative
Release planning is best done as a collaborative effort in my experience by involving the stakeholders and the development team, as the picture below illustrates. To do so, schedule regular roadmapping sessions, possibly as part of your strategy review process and invite key stakeholders and development team members. Additionally, update and discuss the release burndown chart in the sprint review meetings where the same individuals should be present.
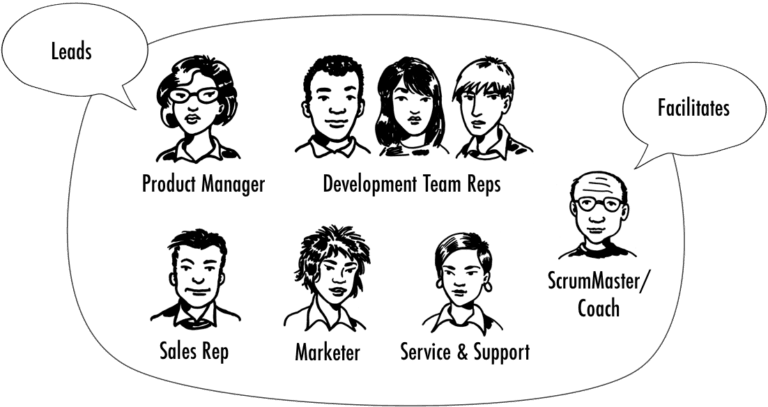
This ensures that the longer-term and short-term release planning decisions are made with the input from the stakeholders and dev team. This tends to lead to better plans, stronger alignment, and increased commitment to implement the decisions.
Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Roman Pichler, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: Release Planning Advice Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |