How to deal with ConcurrentModificationException in Java? Beware while removing elements from ArrayList in loop
One of the common problem while removing elements from an ArrayList in Java is the ConcurrentModificationException. If you use classical for loop with the index or enhanced for loop and try to remove an element from the ArrayList using remove() method, you will get the ConcurrentModificationException but if you use Iterator’s remove method or ListIterator’s
remove() method, then you won’t get this error and be able to remove the element. It’s an unwritten rule in Java that while looping through the list, you should not add() orremove() elements until the collection supports fail-safe Iterator e.g. CopyOnWriteArrayList, which operate on a copy of list rather than the original list.
The main problem with this error is that it confuses developer that list is getting modified by multiple threads and that’s why Java is throwing this error, it’s not true. Most of the time
ConcurrentModificationException comes even without multiple threads modifying the list.
It’s misnomer, don’t get fooled away by this. though it seems natural thinking that maybe some other thread is trying to modify the collection at the same time, it’s usually breaking the Java rule.
In this article, I’ll explain this error and we’ll many code example to reproduce this code even with the single thread and learn how we can avoid concurrent modification error while modifying an ArrayList in Java.
Btw, if you are not familiar with collection classes e.g. ArrayList itself then you should join an online course e.g.
Java Basics: Learn to Code the Right Way on Udemy is a good place to start with.
ConcurrentModificationException in Single Thread
This is the first example of reproducing the concurrent modification exception in Java. In this program, we are iterating over ArrayList using the enhanced foreach loop and removing selective elements e.g. an element which matches certain condition using ArrayList’s remove method.
For example, in the below code we have first added a couple of good programming books e.g. Programming Pearls, Clean Code, Code Complete into ArrayList and then removing any element which has Code in its title.
package beginner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorldApp{
public static void main(String... args){
List<String> listOfBooks = new ArrayList<>();
listOfBooks.add("Programming Pearls");
listOfBooks.add("Clean Code");
listOfBooks.add("Effective Java");
listOfBooks.add("Code Complete");
// Using forEach loop to iterate and removing
// element during iteration will throw
// ConcurrentModificationException in Java
for(String book: listOfBooks){
if(book.contains("Code"));{
listOfBooks.remove(book);
}
}
}
}
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(Unknown Source)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(Unknown Source)
at beginner.HelloWorldApp.main(HelloWorldApp.java:18)You can see that this error comes even though we just have one thread, main thread which is operating with ArrayList. The ConcurrentModification error comes because we are not using Iterator, instead just calling listOfBooks.remove() method.
In this code, I have used Java 1.5 enhanced for loop, you must know how enhanced for loop works in Java.
Difference between for loop and enhanced for loop is that later internally uses an Iterator for going over all elements of a collection. For a more in-depth discussion, see here
Using Classical for loop and ArrayList.remove(index)
Here is another interesting code example of removing elements from ArrayList. Surprisingly this code will not throw ConcurrentModificationException when you first run it? do you know why?
Well, try it before you look at the explanation after the code. It’s really this kind of minor details about Java programming language and Collection framework, which will make you a good developer, and also help you to get your Java certification if you are preparing for it.
package beginner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorldApp{
public static void main(String... args){
List<String> listOfBooks = new ArrayList<>();
listOfBooks.add("Programming Pearls");
listOfBooks.add("Clean Code");
listOfBooks.add("Effective Java");
listOfBooks.add("Code Complete");
System.out.println("List before : " + listOfBooks);
for(int i=0; i<listOfBooks.size(); i++){
String book = listOfBooks.get(i);
if(book.contains("Programming")){
System.out.println("Removing " + book);
listOfBooks.remove(i); // will throw CME
}
}
System.out.println("List after : " + listOfBooks);
}
}
Output
List before : [Programming Pearls, Clean Code, Effective Java, Code Complete]
Removing Programming Pearls
List after : [Clean Code, Effective Java, Code Complete]This code doesn’t throw ConcurrentModificationException because here we are not using Iterator but we are just using traditional for loop.
It’s the Iterator which throws ConcurrentModificationException, and not the remove method of ArrayList, hence you don’t see that error in below code.
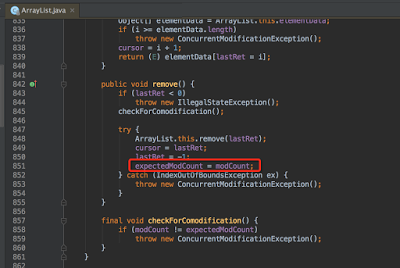
If you look at the code for ArrayList.java, you will notice that there is a nested class which implemented Iterator interface and it’s next() method calls checkForComodification() function which actually checks if ArrayList has modified during iteration or not, if modCount doesn’t match with expectedModCount then it throws ConcurrentModificationException.
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}This kind of questions are also very popular on Oracle Java Certification e.g. OCAJP (1z0-808) and OCPJP (1Z0-809), so if you are preparing for those exams, you should know the answer.
Here is the full code snippet from the ArrayList.java class for your quick reference:
Using Iterator but ArrayList’s remove method
Now, let’s see another code example, where Java programmer thinks he has done everything right but still getting the concurrent modification exception. Can you spot the error? It’s really common and I have seen this kind of code a lot of time on Java forums, StackOverflow and on Facebook Java groups where they asked to fix the problem.
package beginner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorldApp{
public static void main(String... args){
List<String> listOfBooks = new ArrayList<>();
listOfBooks.add("Programming Pearls");
listOfBooks.add("Clean Code");
listOfBooks.add("Effective Java");
listOfBooks.add("Code Complete");
Iterator<String> iterator = listOfBooks.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
String book = iterator.next();
listOfBooks.remove(book);
}
}
}
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(Unknown Source)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(Unknown Source)
at beginner.HelloWorldApp.main(HelloWorldApp.java:18)The real problem with this code is that even though the code is using Iterator to go over ArrayList, it’s not really using the Iterator.remove() method to remove the element. It is just using Iterator to get the next element but calling the ArrayList.remove() method to delete the element.
I know, it looks easy when you know the reason but in real time, many times programmer take even hours to figure out what is wrong. So, just beware of that.
Btw, if you are learning Java then I suggest joining Complete Java Masterclass to learn Java better and avoid such common errors.
Right way to remove element is by using Iterator’s remove method
Finally, here is the right way to delete an element from ArrayList during iteration. In this example, we have used Iterator both iterate as well as remove the element. The code is ok but it has a serious limitation, you can only use this code to remove the current element. You cannot remove any arbitrary element from ArrayList in Java.
package beginner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class HelloWorldApp{
public static void main(String... args){
List<String> listOfBooks = new ArrayList<>();
listOfBooks.add("Programming Pearls");
listOfBooks.add("Clean Code");
listOfBooks.add("Effective Java");
listOfBooks.add("Code Complete");
System.out.println("List before : " + listOfBooks);
Iterator<String> iterator = listOfBooks.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
String book = iterator.next();
System.out.println("Removing " + book);
iterator.remove();
}
System.out.println("List after : " + listOfBooks);
}
}
Output
List before : [Programming Pearls, Clean Code, Effective Java, Code Complete]
Removing Programming Pearls
Removing Clean Code
Removing Effective Java
Removing Code Complete
List after : []The same behavior is applicable to ListIterator as well. I mean you can replace Iterator with ListIterator and code will work fine. The ListIterator also allow you to navigate in both directions i.e. forward and backward.
That’s all about how to avoid ConcurrentModificationException while removing elements from ArrayList during iteration. You can use the same technique to avoid ConcurrentModificationException while removing elements from any other collection classes which have fail-fast Iterator e.g. LinkedList. Btw, if you are new to Java programming then joining a good, comprehensive course like Java Basics: Learn to Code the Right Way on Udemy can help you to learn Java better and quicker.
OtherJava troubleshooting Guides you may like
How to solve ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException in Java? (guide)
How to solve NullPointerException in Java? (guide)
How to solve the “System cannot find the Path specified” error? (solution)
How to solve NoClassDefFoundError while running Java program from a command line? (solution)
How to solve “No JVM found, Please install 64-bit JDK” error in Android Studio? (solution)
How to deal with SQLException “No Suitable driver found ” error in JDBC and MySQL? (guide)
How to solve NumberFormatException in Java? (guide)
How to solve Minecraft – java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: lwjgl64.dll : Access Denied? (solution)
How to fix java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 1 in Java? (solution)
How to fix java.net.SocketException: Software caused connection abort: recv failed (fix)
Thanks for reading this tutorial, if you like this tutorial then please share with your friends and colleagues. If you have any question or suggestion then please drop a comment.
| Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Javin Paul, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: How to deal with ConcurrentModificationException in Java? Beware while removing elements from ArrayList in loop Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |



Hi Paul,
May I know why standard for loop will not throw concurrent modification exception? as there are also we are using ArrayList related remove() method.