Factory Method Design Pattern Example
This article is part of our Academy Course titled Java Design Patterns.
In this course you will delve into a vast number of Design Patterns and see how those are implemented and utilized in Java. You will understand the reasons why patterns are so important and learn when and how to apply each one of them. Check it out here!
Table Of Contents
1. Introduction
In today’s modern world, everyone is using software to facilitate their jobs. Recently, a product company has shifted the way they used to take orders from their clients. The company is now looking to use an application to take orders from them. They receive orders, errors in orders, feedback for the previous order, and responses to the order in an XML format. The company has asked you to develop an application to parse the XML and display the result to them.
The main challenge for you is to parse an XML and display its content to the user. There are different XML formats depending on the different types of messages the company receives from its clients. Like, for example, an order type XML has different sets of xml tags as compared to the response or error XML. But the core job is the same; that is, to display to the user the message being carried in these XMLs.
Although the core job is the same, the object that would be used varies according to the kind of XML the application gets from the user. So, an application object may only know that it needs to access a class from within the class hierarchy (hierarchy of different parsers), but does not know exactly which class from among the set of subclasses of the parent class is to be selected.
In this case, it is better to provide a factory, i.e. a factory to create parsers, and at runtime a parser gets instantiated to do the job, according to the kind of XML the application receives from the user.
The Factory Method Pattern, suited for this situation, defines an interface for creating an object, but let subclasses decide which class to instantiate. Factory Method lets a class defer instantiation to subclasses.
Let us see some more details about the Factory Method Pattern and then we will use it to implement the XML parser for the application.
2. What is the Factory Method Pattern
The Factory Method Pattern gives us a way to encapsulate the instantiations of concrete types. The Factory Method pattern encapsulates the functionality required to select and instantiate an appropriate class, inside a designated method referred to as a factory method. The Factory Method selects an appropriate class from a class hierarchy based on the application context and other influencing factors. It then instantiates the selected class and returns it as an instance of the parent class type.
The advantage of this approach is that the application objects can make use of the factory method to get access to the appropriate class instance. This eliminates the need for an application object to deal with the varying class selection criteria.
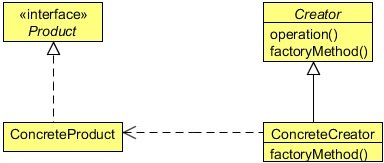
Product
- Defines the interface of objects the factory method creates.
ConcreteProduct
- Implements the Product interface.
Creator
- Declares the factory method, which returns an object of type Product. Creator may also define a default implementation of the factory method that returns a default ConcreteProduct object.
- May call the factory method to create a Product object.
ConcreteCreator
- Overrides the factory method to return an instance of a ConcreteProduct.
Factory methods eliminate the need to bind application-specific classes into your code. The code only deals with the Product interface; therefore it can work with any user-defined ConcreteProduct classes.
3. Implementing Factory Method Pattern
To implement the solution for the application as discussed above, let’s first check the product we have.
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public interface XMLParser {
public String parse();
}
The above interface will be used by the different XML parsers.
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class ErrorXMLParser implements XMLParser{
@Override
public String parse() {
System.out.println("Parsing error XML...");
return "Error XML Message";
}
}
The ErrorXMLParser implements the XMLParser and is used to parse the error message XMLs.
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class FeedbackXML implements XMLParser{
@Override
public String parse() {
System.out.println("Parsing feedback XML...");
return "Feedback XML Message";
}
}
The above class is used to parse the feedback message XMLs.
The other XML parsers are:
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class OrderXMLParser implements XMLParser{
@Override
public String parse() {
System.out.println("Parsing order XML...");
return "Order XML Message";
}
}
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class ResponseXMLParser implements XMLParser{
@Override
public String parse() {
System.out.println("Parsing response XML...");
return "Response XML Message";
}
}
To display the parsed messages from the parsers, an abstract service class is created which will be extends by service specific, i.e. parser specific, display classes.
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public abstract class DisplayService {
public void display(){
XMLParser parser = getParser();
String msg = parser.parse();
System.out.println(msg);
}
protected abstract XMLParser getParser();
}
The above class is used to display the message fetched by the XML parser to the user. The above class is an abstract class that contains two important methods. The display method is used to display the message to the user. The getParser method is the factory method which is implemented by the subclasses to instantiate the parser object and the method is used by the display method in order to parse the XML and gets the message to display.
Below are the subclasses of the
DisplayService which implement the getParser method.
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class ErrorXMLDisplayService extends DisplayService{
@Override
public XMLParser getParser() {
return new ErrorXMLParser();
}
}
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class FeedbackXMLDisplayService extends DisplayService{
@Override
public XMLParser getParser() {
return new FeedbackXML();
}
}
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class OrderXMLDisplayService extends DisplayService{
@Override
public XMLParser getParser() {
return new OrderXMLParser();
}
}
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class ResponseXMLDisplayService extends DisplayService{
@Override
public XMLParser getParser() {
return new ResponseXMLParser();
}
}
Now, let’s test the factory method.
package com.javacodegeeks.patterns.factorymethodpattern;
public class TestFactoryMethodPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DisplayService service = new FeedbackXMLDisplayService();
service.display();
service = new ErrorXMLDisplayService();
service.display();
service = new OrderXMLDisplayService();
service.display();
service = new ResponseXMLDisplayService();
service.display();
}
}
The above class results to the following output:
Parsing feedback XML... Feedback XML Message Parsing error XML... Error XML Message Parsing order XML... Order XML Message Parsing response XML... Response XML Message
In the above class, you can clearly see that the by letting the subclasses to implement the factory method creates the different instances of parsers which can be used at runtime according to the need.
4. When to use the Factory Method Pattern
Use the Factory Method pattern when
- A class can’t anticipate the class of objects it must create.
- A class wants its subclasses to specify the objects it creates.
- Classes delegate responsibility to one of several helper subclasses, and you want to localize the knowledge of which helper subclass is the delegate.
5. Factory Method Pattern in JDK
The following are the usage(s) of the Factory Method Pattern in JDK.
java.util.Calendar#getInstance()java.util.ResourceBundle#getBundle()java.text.NumberFormat#getInstance()java.nio.charset.Charset#forName()java.net.URLStreamHandlerFactory#createURLStreamHandler(String)(Returns singleton object per protocol)
6. Download the Source Code
This was a lesson on the Factory Method Pattern. You may download the source code here:
FactoryMethodPattern-Project




It doesn’t look like factory method, more like abstract factory. Where are static calls?