Application Auto Scaling on AWS – Options and Impact on Performance
It is essential to scale software applications to avoid performance bottlenecks with increased work load due to may be increase in customer base to the website or an application that need to process large dataset etc.. Cloud providers are usually the best way to get access to additional on-demand resources to scale up or scale down based on load variations on application.
1. What is Scalability?
Scalability is a characteristic where a solution can handle increased work load or transactions in a capable manner with addition of compute and storage resources. If your current solution is working for 1 million simultaneous users, a software that is highly scalable would work well for billions of users with the addition of additional resources. To handle more load, there are two types of Scaling, Vertical Scaling and Horizontal Scaling
1.1 Vertical Scaling (Or Scaling up)
In this type of scaling, you add more advanced hardware with increased capacity like more RAM, powerful Processor etc. to serve increased load on your application. The issue with Vertical Scaling is that there is always a limit on how much the capacity can grow. This type of scaling is expensive due to hardware cost and takes time to get new hardware. If you want to quickly scale your application for increased load, this type of scaling isn’t a great choice.
1.2 Horizontal Scaling (Or Scaling Out)
In this type of scaling, you can add more servers to the existing capacity to serve increased load on your application. Increased load on application is spread across all the servers in the cluster through a Load Balancer. This type of scaling is best choice if you want to grow your software quickly and it isn’t expensive.
It’s easy to scale applications in Cloud
Environments through configuration change, which automatically adds additional servers
to the cluster based on the performance monitoring metrics.
It’s easy to scale applications in Cloud Environments through configuration change, which automatically adds additional servers to the cluster based on the performance monitoring metrics. In this Article, we’ll discuss different Autoscaling options available for autoscaling AWS EC2 Auto Scaling group in AWS Cloud Environment.
2. What is Auto Scaling?
Autoscaling is a feature in cloud computing environment that automatically adds or removes compute resources such as Virtual Machines from instance cluster when usage metrics meet the configured thresholds. Autoscaling or dynamic scaling feature ensures that new compute resources are be added to the cluster seamlessly to meet spike in demand spikes and terminate the instances when the demand drops.
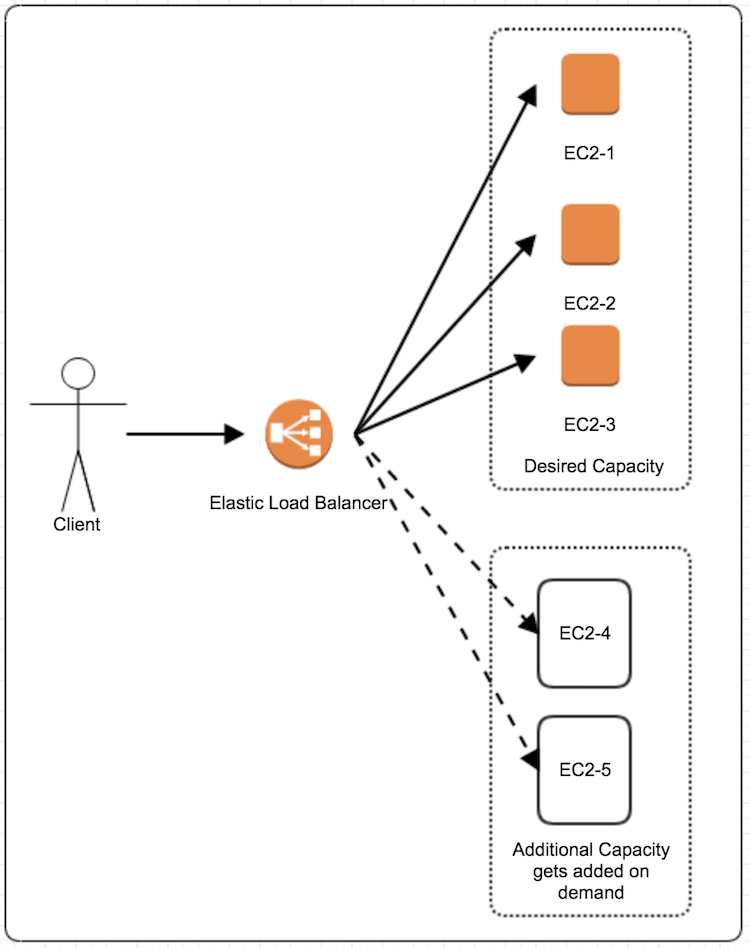
3. Why do you need Autoscaling?
Autoscaling helps in achieving
better and consistent performance irrespective of the load on the application.
Auto scaling also helps in reducing the costs by automatically terminating the
resources when there is less demand.
With Autoscaling, you can configure how many servers are to be added or removed when demand threshold is met. Also, you can configure the max number of servers that can be added to the cluster. No data should be stored on the instance that is part of Autoscaling group, instead persist data to a distributed storage system.
4. Auto Scaling Components
Follow the steps outlined here for creating Autoscaling Group from AWS Console. Following are major components of autoscaling.
EC2 Instance: EC2 is a virtual server in Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud environment for running applications. EC2 instances are created from AMIs (Amazon Machine Images).
Auto Scaling Group (ASG): ASG is a collection of EC2 instance with similar characteristics and are created from the same AMI. With auto scaling, instances can be added or removed dynamically from Autoscaling Group depending on the load. Autoscaling group maintains desired number of instances by performing periodic health checks. If any unhealthy instance is found, ASG terminates this unhealthy instance and launches new one.
Launch Configuration: Launch Configuration is a template used by ASG to launch EC2 instances. In Launch Configuration you need to specify AMI Id, Instance Type, a Key pair, Security Groups etc. You can use same launch configuration for creating multiple autoscaling groups.
Scaling Criteria: Scaling criteria configuration instructs ASG about when and how to scale.
5. different types of Auto Scaling on AWS?
Following are three different types of autoscaling options available on AWS cloud environment:
5.1 Reactive Autoscaling
In Reactive Scaling, you define the scaling criteria to scale in response to change in demand. Scaling of Amazon EC2 instances in Auto Scaling group (ASG) is done based on average CPU consumption, or Memory usage of the EC2 instances (based on Cloud watch Metrics) etc. For e.g if you don’t want the CPU utilization of the ASG to exceed 80%, you can set scaling criteria to scale automatically when this threshold is met. When the configured threshold is met, new EC2 instances are added or existing EC2 instances are removed from ASG.
5.2 Proactive Autoscaling
Proactive Autoscaling is a mechanism of scheduling EC2 instances for predictable load changes based on the historical observation of periodic spikes in traffic to ASG. For e.g if your video application has a higher usage during primetime (say 6pm – 9 pm) then you can schedule autoscaling to add additional instances right before 6 pm and terminate additional instances right after 9 pm.
To create Proactive autoscaling
group, you need to create a schedule action with start time when the action
should take effect, Min, Max and desired capacity. Schedule action tells ASG to
perform Scale-out or Scale-in action at specified time.
Follow these steps for created Proactive or Scheduled autoscaling.
5.3 Predictive Autoscaling
Right before AWS re:Invent 2018, AWS
introduced the most anticipated feature for AWS EC2, Predictive Scaling. With Predictive Scaling
EC2 instances capacity can be scaled ahead of traffic changes.
Predictive Auto Scaling is based on the trained Machine Learning (ML) Algorithm that works with time-series data. This trained ML Algorithm predicts expected traffic and EC2 usage based on the data from your actual EC2 usage and billions of data points drawn from AWS observation. The model needs at least one day’s of historical data to start making predictions; it is re-evaluated every 24 hours to create a forecast for the next 48 hours. The ML model gets better with time as it learns from actual usage data generated by Autoscaling group.
Predictive Auto Scaling can be enabled with a single click. With proactive scaling, over-provisioning of EC2 resources can be avoided, which will reduce EC2 costs. A buffer can be set in predictive scaling, so newly launched instances can warm up before ready to handle the traffic at the predicted time. There is no cost associated with using predictive scaling feature. Predictive autoscaling helps in optimizing the EC2 costs and is a great fit for applications where the load spike is periodic.
Configuring Predictive Scaling plan:
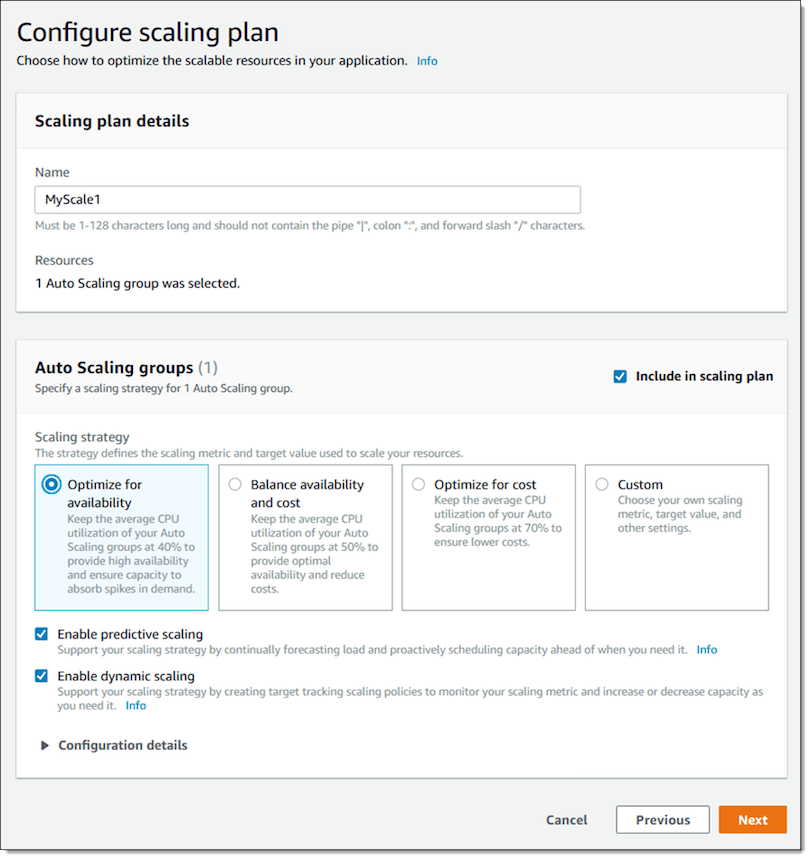
Source: AWS Blog
You can use Predictive scaling and Dynamic scaling together. Predictive scaling helps with forecasting and dynamic scaling helps in scaling-out based on cloud watch metric. You can forecast based on pre-populated metric or by custom metric.
Sample forecast based on CPU Utilization metric.
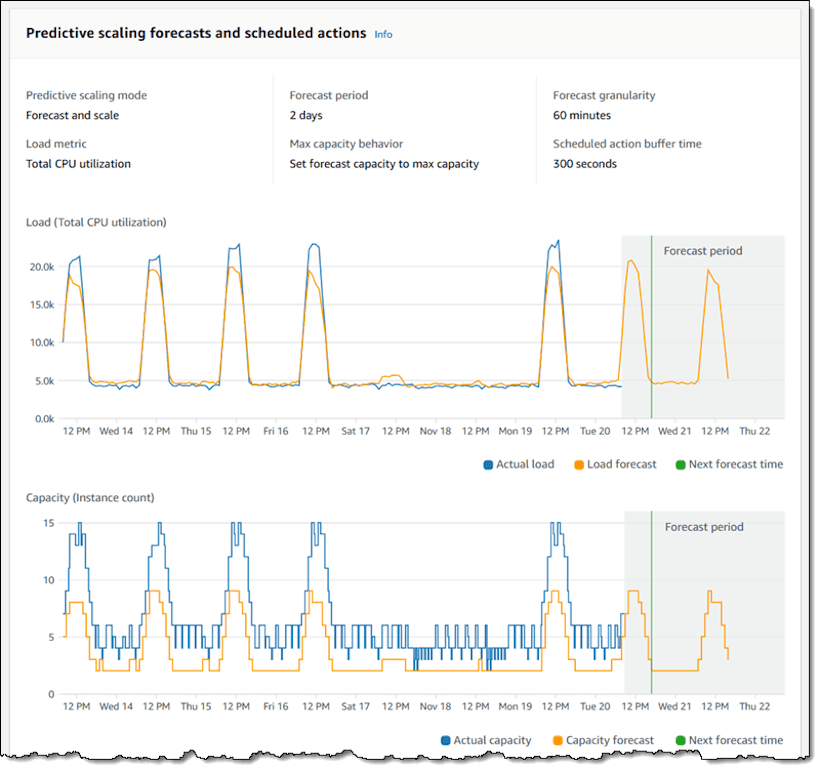
Source: AWS Blog
Note: Predictive Auto Scaling is available in US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), US West (Oregon), Europe (Ireland), and Asia Pacific (Singapore) Regions
6. Summary
Autoscaling is a powerful feature for addressing performance bottlenecks in the applications when the load on application varies. It also helps in saving costs by terminating instances from the Autoscaling group when there is less demand for application. Predictive autoscaling helps predict the load ahead and scale the fleet accordingly without manual intervention by leveraging historical fleet usage metric.





