Do Primitives Need To Go?
I am currently working on an enterprise application using JSF as the view technology and JPA for the persistence layer. It may have been something in a backing bean or service method, but it struck me: Is there a good reason to use primitives anymore in enterprise applications?
When I started programming with Java around J2SE 1.2 (or was it J2SE 5.0, or maybe Java 2?), I only used primitives in my code. At that time, I thought it was nice I could rely on the default values instead of having to initialize something before I could use it. I didn’t know too much about wrappers at the time, and didn’t think I had a good reason to look into them any further.
I don’t have any clear memories of when I started to use the primitive wrappers, but I do remember when JDK 1.5 allowed for the automatic conversions between primitives and their respective primitive wrapper classes or commonly known as autoboxing/unboxing. This was nice as it didn’t matter if an int was passed to a method requiring an Integer or vice versa. It was syntactic sugar that seemingly made programming a little easier.
Frameworks
Even though Java enterprise frameworks such as JSF and JPA do a lot of work for you, it also exposes some of the weaknesses of relying on autoboxing and primitives.
These frameworks rely on the use of the primitive wrapper class instead of the respective primitive. If you use the JPA tool to create an entity based on an existing table, the tool will use the wrapper for the variable type. JSF inputs and converters operate on objects. With JPA, it has to. Remember the primitive defaults? A primitive’s default value can be confused with what is stored in the database.
If long was used as a simple entity id, the entity would have a default value of 0L. 0L is technically a value, so it makes it difficult to know whether the entity has been persisted or not. If id is of type Long, then it is easy to tell if the entity has been persisted since the id can now be null and therefore representing an un-persisted entity.
//id is long and entity is not persisted long id = entity.getId(); //value of 0L Long id = entity.getId(); //doesn’t help, still 0L //id is Long and entity is not persisted Long id = entity.getId(); //null long id = entity.getId(); //what happens here? //reference: https://keyholesoftware.com/2014/10/13/java-and-the-sweet-science/
Type Context
Primitive types do not adequately express the semantic context of the value. Let’s say we retrieve today’s temperature from a service and the returned value representing degrees is an int. Is it easy to determine what the context of int degrees is?
First, is the value represented in celsius or fahrenheit? Second, what if the value is 0? You would have to assume the value was actually set and it isn’t the default value of 0. You may wonder why it feels like 70 degrees outside when the service says it’s 0.
Instead of using a primitive or even a primitive wrapper, the best solution may be to use a custom object that resolves to a proper value. For our value representing temperature, we could create a Fahrenheit object. This object would remove all doubt on the context of the value.
//
public class Fahrenheit {
…
private Integer degrees;
…
}
Fahrenheit f = temperatureService.getDegrees(today);
//A developer wouldn’t be able to accidently pass in a Celsius object when the method is expecting Fahrenheit.
//
…
public Celsius convertDegrees(Fahrenheit f) {
…
}
//only this would work
Celsius c = temperatureService.convertDegrees(f);
//Using a primitive as a return value can also be ambiguous. Returning a boolean to represent if something worked or not doesn’t necessarily represent what did happen. Using a Result object is more descriptive by containing more information.
Mocking
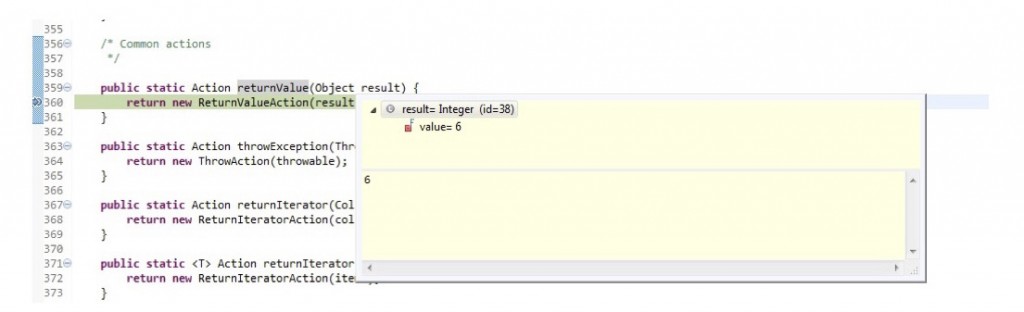
While mocking frameworks can handle primitives, mocking frameworks like to work with objects. The code snippet below is the the Expectations class in JMock. As the code snippet shows below, some autoboxing magic is allowing the framework to set the expectation that a int value of 6 will be returned.
Expectations.returnValue(Object result):
context.checking(new Expectations() {
{
atLeast(1).of(serviceMock).getPrimitive(5);
will(returnValue(6));
….
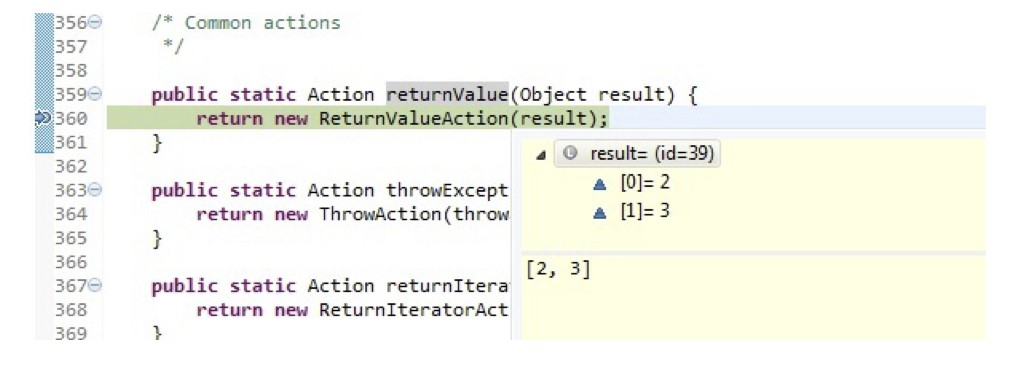
}JMock seems to handle primitive arrays properly since the object for arrays is dynamically created.
Expectations.returnValue(Object result):
context.checking(new Expectations() {
{
int[] ints = { 2, 3 };
atLeast(1).of(serviceMock).getPrimitives(5);
will(returnValue(ints));
….
}Even though primitives and primitive arrays worked with mocking frameworks, it feels like you are not working with the real values. Your parameter is an int, but the mocking framework would like you to use Integer.
Thoughts
Looking back at the history of the primitive wrappers, the increased functionality of the wrappers over time, autoboxing/unboxing, and reading articles from developers from other languages, it feels like primitives could have been left out of the initial implementation of Java. Java is an object-oriented language, but contains non-object primitives. The autoboxing feature feels more like a band-aid than a real solution.
I am making this specific to enterprise applications due to the fact that enterprise applications have access to generous amounts of resources. The environment makes it easier to create descriptive code that use of objects like Integer and Fahrenheit. In constrained devices where garbage collection costs and heap size matter, primitives make sense and hold an advantage over object counterparts.
| Reference: | Do Primitives Need To Go? from our JCG partner John Hoestje at the Keyhole Software blog. |



There are some advantages and disadvantages of using boxed primitives over primitives. Effective Java spells out the disadvantages of boxed primitives in “Item 49: Prefer primitive types to boxed primitives”. Why waste time and memory in instances where a primitive would suffice? If you need to support the concept of null values, such as in your JPA example, you should be using boxed primitives. This behavior may be too late to change at this point, in which case I think it’s best that Java developers simply learn how primitives behave in the language, and use boxed primitives only when necessary.… Read more »
This is all about what you work on. If you making a transactionnal application, often it is business logic that dominate. You’d want to ensure this is as clean and good as possible. If you think the native come in the way, you can get ride of it. There no real impact. If you have some heavy algorithm going on, there something very difference in term of performance between working on a array of native or working on an array ob object, each with their own Integer and extra unecessary data (like the unit of a temperature). I just had… Read more »
I appreciate your argument of favoring clean abstractions over concrete types. For instance, common practice is to prefer Lists over Arrays unless performance demands it. There are many conveniences that Lists offer over Arrays that justify the overhead in most circumstances. I don’t think this applies to boxed primitives, though. Boxed primitives have other disadvantages ignoring the performance overhead. One advantage regular primitives have is that they can’t be null. This is a valuable trait! Let’s take the simplest type boolean for example — booleans have 2 possible states, perfect for use in 2-value logic. The boxed type Boolean, however,… Read more »