9 Differences between TCP and UDP Protocol – Java Network Interview Question
TCP and UDP are two transport layer protocols, which are extensively used in internet for transmitting data between one host to another. Good knowledge of how TCP and UDP works is essential for any programmer. That’s why differences between TCP and UDP is a popular Java programming interview question. I have seen this question many times on various Java interviews , especially for server side Java developer positions. Since FIX (Financial Information Exchange) protocol is also a TCP based protocol, several investment banks, hedge funds, and exchange solution providers look for Java developers with good knowledge of TCP and UDP. Writing FIX engines and server side components for high speed electronic trading platforms requires capable developers with a solid understanding of the fundamentals including data structure, algorithms and networking.
By the way, use of TCP and UDP is not limited to one area, it’s at the heart of internet. The protocol which is core of internet, HTTP is based on TCP. One more reason, why a Java developer should understand these two protocols in detail is that Java is extensively used to write multi-threaded, concurrent and scalable servers. Java also provides a rich Socket programming API for both TCP and UDP based communication. In this article, we will learn the key differences between the TCP and UDP protocols. To start with, TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol, and both are used extensively to build Internet applications.
Differences between TCP vs UDP Protocol
I love to compare two things on different points, this not only makes them easy to compare but also makes it easy to remember differences. When we compare TCP to UDP, we learn difference in how both TCP and UDP works, we learn which one provides reliable and guaranteed delivery and which doesn’t. Which protocol is fast and why, and most importantly when to choose TCP over UDP while building your own distributed application. In this article we will see difference between UDP and TCP in 9 points, e.g. connection set-up, reliability, ordering, speed, overhead, header size, congestion control, application, different protocols based upon TCP and UDP and how they transfer data.
- Connection oriented vs Connection less
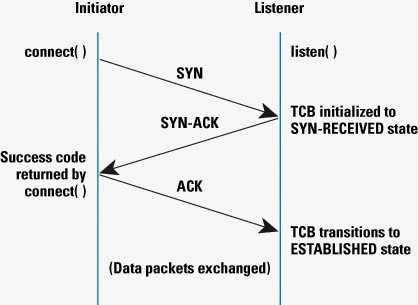 The first and foremost difference between them is that TCP is a connection oriented protocol while UDP is a connection-less protocol. This means a connection is established between client and server, before they can send data over TCP. Connection establishment process is also known as TCP hand shaking where control messages are interchanged between client and server. The image here describes the process of a TCP handshake, where control messages are exchanged between client and server. Client, which is the initiator of TCP connection, sends a SYN message to the server, which is listening on a TCP port. Server receives and sends a SYN-ACK message, which is received by client again and responded using ACK. Once the server receive this ACK message, the TCP connection is established and ready for data transmission. On the other hand, UDP is a connection less protocol, and point to point connection is not established before sending messages. That’s the reason why, UDP is more suitable for multicast distribution of message, one to many distribution of data in single transmission.
The first and foremost difference between them is that TCP is a connection oriented protocol while UDP is a connection-less protocol. This means a connection is established between client and server, before they can send data over TCP. Connection establishment process is also known as TCP hand shaking where control messages are interchanged between client and server. The image here describes the process of a TCP handshake, where control messages are exchanged between client and server. Client, which is the initiator of TCP connection, sends a SYN message to the server, which is listening on a TCP port. Server receives and sends a SYN-ACK message, which is received by client again and responded using ACK. Once the server receive this ACK message, the TCP connection is established and ready for data transmission. On the other hand, UDP is a connection less protocol, and point to point connection is not established before sending messages. That’s the reason why, UDP is more suitable for multicast distribution of message, one to many distribution of data in single transmission.
- Reliability
TCP provides delivery guarantee, which means a message sent using TCP protocol is guaranteed to be delivered to the client. If a message is lost in transit then it is recovered using resending, which is handled by the TCP protocol itself. On the other hand, UDP is unreliable, it doesn’t provide any delivery guarantee. A datagram package may be lost in transit. That’s why UDP is not suitable for programs which require guaranteed delivery.
- Ordering
Apart from delivery guarantee, TCP also guarantees order of message. The messages will be delivered to the client in the same order that the server has sent them, though its possible they may reach out of order to the other end of the network. TCP protocol will do all the sequencing and ordering for you. UDP doesn’t provide any ordering or sequencing guarantee. Datagram packets may arrive in any order. That’s why TCP is suitable for application which need delivery in sequenced manner, though there are UDP based protocols as well which provide ordering and reliability by using sequence number and redelivery e.g. TIBCO Rendezvous, which is actually a UDP based application.
- Data Boundary
TCP does not preserve data boundary, UDP does. In Transmission control protocol, data is sent as a byte stream, and no distinguishing indications are transmitted to signal message (segment) boundaries. On UDP, Packets are sent individually and are checked for integrity only if they arrived. Packets have definite boundaries which are honoured upon receipt, meaning a read operation at the receiver socket will yield an entire message as it was originally sent. Though TCP will also deliver complete message after assembling all bytes. Messages are stored on TCP buffers before sending to make optimum use of network bandwidth.
- Speed
In one word, TCP is slow and UDP is fast. Since TCP does has to create connection, ensure guaranteed and ordered delivery, it does lot more than UDP. This costs TCP in terms of speed, that’s why UDP is more suitable where speed is a concern, for example online video streaming, telecast or online multi player games.
- Heavy weight vs Light weight
Because of the overhead mentioned above, Transmission control protocol is considered as heavy weight as compared to light weight UDP protocol. The simple mantra of UDP is to deliver messages without bearing any overhead of creating a connection and guaranteeing delivery or order guarantee. This is also reflected in their header sizes, which is used to carry meta data.
- Header size
TCP has a bigger header than UDP. Usual header size of a TCP packet is 20 bytes which is more than double of 8 bytes, header size of UDP datagram packet. TCP header contains Sequence Number, Ack number, Data offset, Reserved, Control bit, Window, Urgent Pointer, Options, Padding, Check Sum, Source port, and Destination port. While UDP header only contains Length, Source port, Destination port, and Check Sum. Here is how TCP and UDP header looks like :
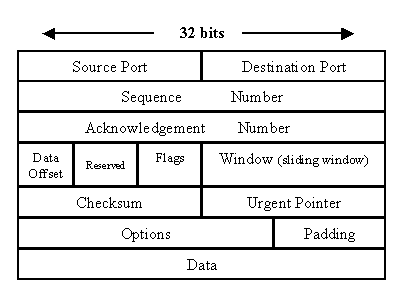
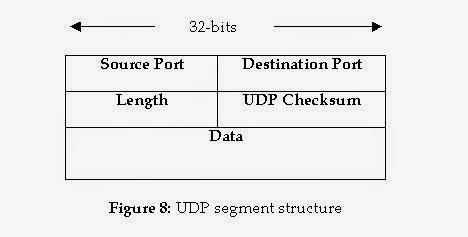
- Congestion or Flow control
TCP does Flow Control. TCP requires three packets to set up a socket connection, before any user data can be sent. TCP handles reliability and congestion control. On the other hand, UDP does not have an option for flow control.
- Usage and application
Where does TCP and UDP are used in internet? After knowing key differences between TCP and UDP, we can easily conclude, which situation suits them. Since TCP provides delivery and sequencing guaranty, it is best suited for applications that require high reliability, and transmission time is relatively less critical. While UDP is more suitable for applications that need fast, efficient transmission, such as games. UDP’s stateless nature is also useful for servers that answer small queries from huge numbers of clients. In practice, TCP is used in the finance domain e.g. the FIX protocol is a TCP based protocol, while UDP is used heavily in gaming and entertainment sites.
- TCP and UDP based Protocols
One of the best example of TCP based higher end protocol is HTTP and HTTPS, which is everywhere on internet. In fact most of the common protocols you are familiar of e.g. Telnet, FTP and SMTP all are based over Transmission Control Protocol. UDP don’t have anything as popular as HTTP but it is also extensively used in protocol like DHCP and DNS. Some of the other protocols which are based on the User Datagram protocol are Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), TFTP, BOOTP and NFS (early versions).
Always remember to mention that TCP is connection oriented, reliable, slow, provides guaranteed delivery and preservers order of messages, while UDP is connection less, unreliable, no ordering guarantee, but a fast protocol. TCP overhead is also much higher than UDP, as it transmits more meta data per packet than UDP. It’s worth mentioning that header size of Transmission control protocol is 20 bytes, compared to 8 bytes header of User Datagram protocol. Use TCP, if you can’t afford to lose any message, while UDP is better for high speed data transmission, where loss of single packet is acceptable e.g. video streaming or online multi player games. While working in TCP/UDP based application on Linux, it’s also good to remember basic networking commands e.g. telnet and netstat, they help tremendously to debug or troubleshoot any connection issue.
| Reference: | 9 Difference between TCP and UDP Protocol – Java Network Interview Question from our JCG partner Javin Paul at the Javarevisited blog. |




